Atlante
News
Achieving Climate Neutrality: How the EU is Paving the Way for a Greener Future

8 November 2024
What is Climate Neutrality?
Climate neutrality means achieving a balance between greenhouse gas emissions and removal efforts, leading to net-zero emissions. Achieving this involves reducing emissions as much as possible and offsetting remaining ones through carbon capture, reforestation, and other nature-based solutions. The EU’s goal of climate neutrality by 2050 requires a broad strategy—transitioning to renewable energy and building global partnerships to counter climate change and ensure a sustainable future.
5 Key Facts About the EU’s Path to Climate Neutrality by 2050
The EU is committed to becoming climate-neutral by 2050, aiming to reduce or offset all greenhouse gas emissions. Here’s how the EU is tackling this ambitious goal:
- Greenhouse Gas Reduction Targets: The EU has set mandatory emissions reduction targets for 2030 and 2050.
- Legislative Support: Policies like the European Green Deal provide frameworks for sustainable economic growth.
- Energy Transition: Heavy investments are directed toward renewable energy sources and boosting energy efficiency.
- Research and Innovation: Funding supports the development of clean technologies.
- Global Partnerships: The EU collaborates internationally to advance climate action.
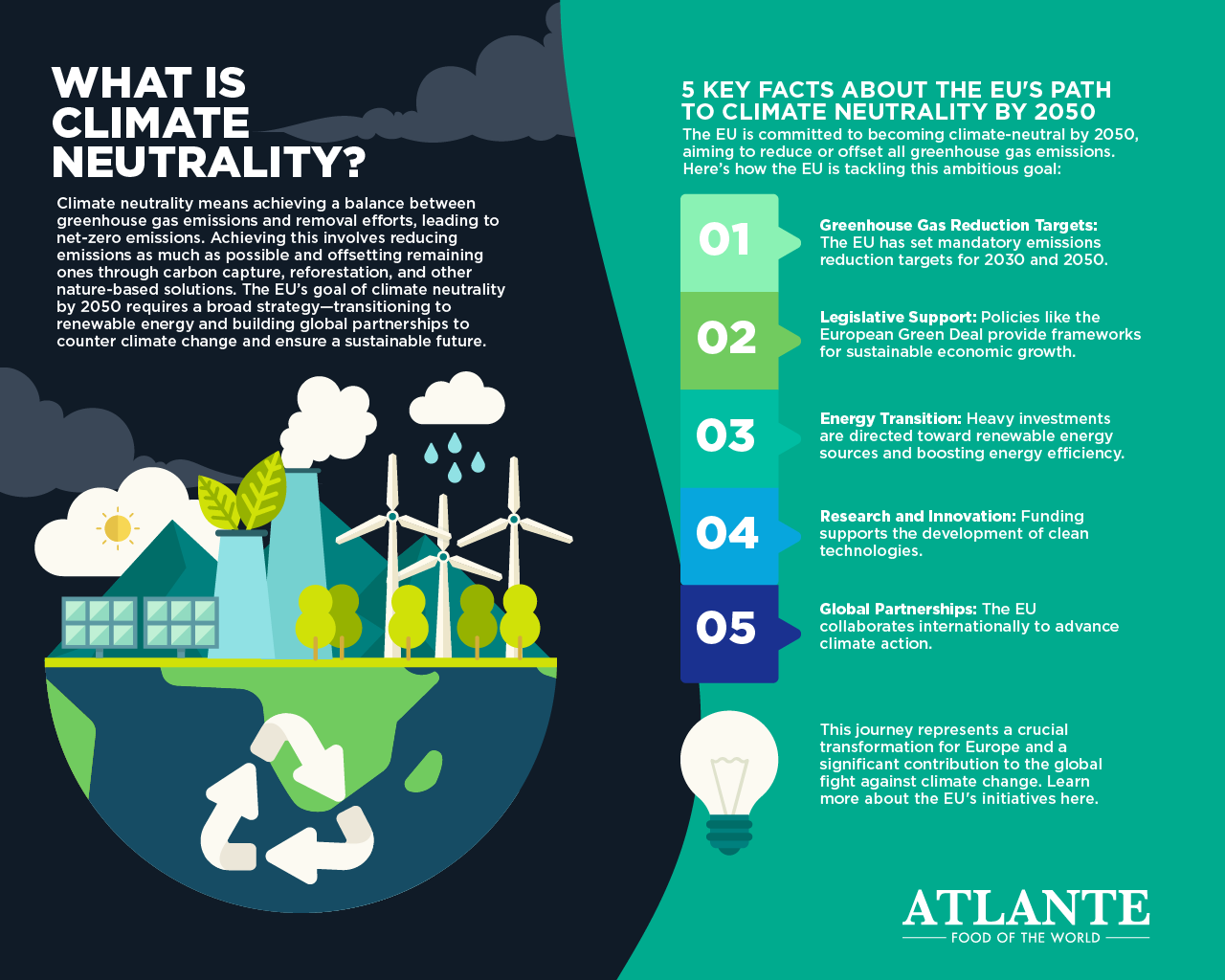
This journey represents a crucial transformation for Europe and a significant contribution to the global fight against climate change. Learn more about the EU’s initiatives here.





